Hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) testing for ADAS smart cameras
Smart cameras account for a large proportion of installed vehicles in China, and compared with high-end solutions, they have the characteristics of low cost and simple functions. How to achieve more visual functions at less cost is the core competitive proposition of smart cameras. Under this proposition, related HIL test requirements were born, including link connectivity, perception fusion and recognition results, automatic cycle control (ACC), and automatic emergency braking (AEB).
There is a clear difference in the architecture of smart cameras and high-end autonomous driving cameras. Compared with the architecture of the ECU and camera in the high-end autonomous driving camera, the smart camera adopts the architecture of ECU and camera integration. The HIL system is mainly composed of a scene server, a PXI real-time machine and a test piece.
Smart camera HIL test system architecture
NI's dedicated HIL test solution for smart cameras uses NIVeriStand software and NIPXI hardware as the classic overall framework, using the link from the scene simulation software to RDMA to provide video data simulation, and using the PXle1486/7/8/9 video simulation module and the universal MIPI adapter box developed by the NI China team as the simulation interface.
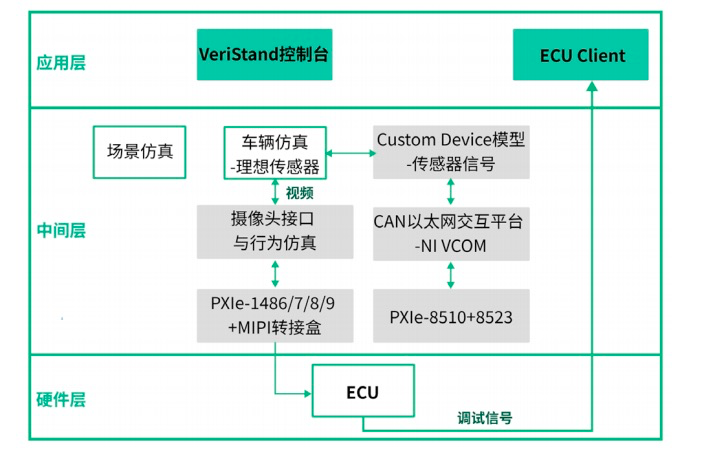
Nl VeriStand software is the main control interface of the whole system, and in terms of software architecture, it uses a classic three-layer design structure, which is composed of hardware layer, middle layer, and application layer.
VeriStand software can either write a CustomDevice model that runs in the middle tier or act as a console host at the application layer. Users can operate the Veristand main interface for start-stop control and signal monitoring for HIL tasks. At the same time, the solution also supports API control, and users can further integrate for automation.


